You are here: Home > Basic and Advanced Life Support
Basic and Advanced Life Support
- Adult Basic Life Support (BLS) Algorithm
- Glasgow Coma Scale
- Revised Trauma Score
- ATLS Hemorrhage Classification
- ACLS Algorithms
- See also: Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support
- See also: Key Acute Care Adult Medications
- See also: Key Acute Care Pediatric Medications
Adult Basic Life Support (BLS) Algorithm
Adult BLS Health Providers
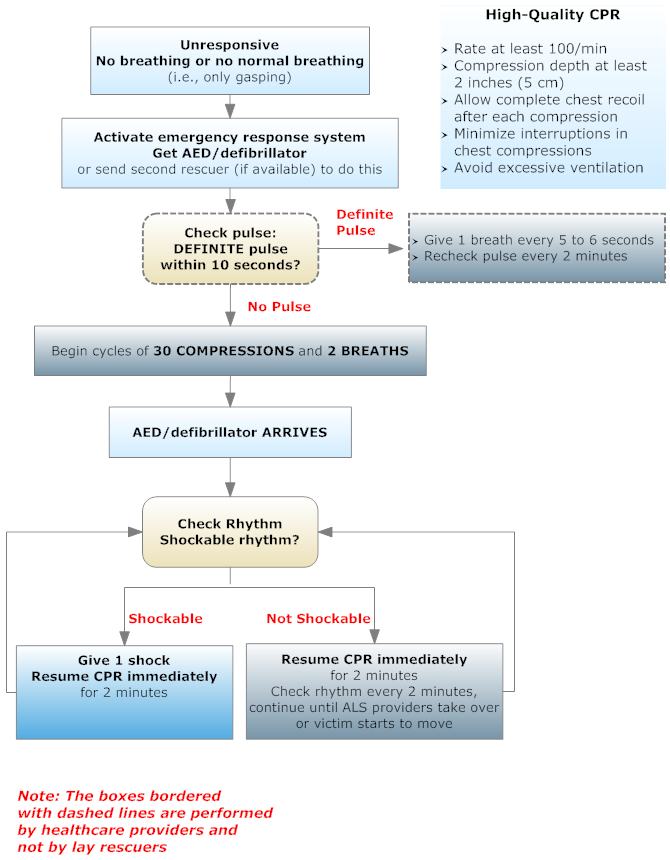
See also:
- Simplified Adult BLS Algorithm (American Heart Association, 2010)
- BLS Adult Basic Life Support Algorithm for Healthcare Providers (American Heart Association, 2010)
Adapted from: Berg RA, Hemphill R, Abella BS, Aufderheide TP, Cave DM, Hazinski MF, Lerner EB, Rea TD, Sayre MR, Swor RA. Part 5: adult basic life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2010 Nov 2;122(18 Suppl 3):S685-705.
Glasgow Coma Scale
| Behavior | Response | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Eye opening | Spontaneous To speech To pain None |
4 3 2 1 |
| Best verbal response | Oriented Confused Inappropriate Words Incomprehensible sounds None |
5 4 3 2 1 |
| Best motor response | Obeys Localizes Withdraws Abnormal flexion to pain Extensor response to pain None |
6 5 4 3 2 1 |
Revised Trauma Score
The Revised Trauma Score (RTS) is made up of a combination of results from three categories:
- Glasgow Coma Scale
- Systolic Blood Pressure
- Respiratory rate
The score range is 0-12. In START triage, a patient with an RTS score of
- 12 is labeled DELAYED (walking wounded)
- 11 is URGENT (intervention is required but the patient can wait a short time)
- 10-3 is IMMEDIATE (immediate intervention is necessary)
- <3 is MORGUE, which is given to seriously injured people. These people should not receive certain care because they are unlikely to survive. The reasoning is that diverting scarce resources away from people with a little chance of survival increases the chances of survival of others who are inherently more likely to survive.
| Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) | Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | Respiratory Rate (breaths/min) | Coded Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13-15 | >89 | 10-29 | 4 |
| 9-12 | 76-89 | >29 | 3 |
| 6-8 | 50-75 | 6-9 | 2 |
| 4-5 | 1-49 | 1-5 | 1 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Add the value of each characteristic. Highest possible total score is 12, and the lowest possible total score is 0.
Champion et al., A Revision of the Trauma Score. Journal of Trauma. 1989:29(5): pg. 623-9
ATLS Hemorrhage Classification
| Estimated Blood Loss Based on Patient's Initial Presentation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Class I | Class II | Class III | Class IV |
| Blood loss (ml) | Up to 750 | 750-1500 | 1500-2000 | >2000 |
| Blood loss (% blood volume) | Up to 15 | 15-30 | 30-40 | >40 |
| Pulse Rate (bpm) | <100 | 100-120 | 120-140 | >140 |
| Blood Pressure | Normal | Normal | Decreased | Decreased |
| Pulse Pressure (mmHg) | Normal or increased | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased |
| Respiratory Rate (breaths/min) | 14-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | >35 |
| Urine Output | >30 | 20-30 | 5-15 | Neglible |
| CNS/Mental status | Slightly anxious | Mildly anxious | Anxious, confused | Confused, lethargic |
| Fluid replacement | Crystalloid | Crystalloid | Crystalloid and blood | Crystalloid and blood |
For a 70kg male
Taken from ATLS handbook
ACLS Algorithms
- ACLS Basic Life Support (BLS) Primary Survey for Respiratory Arrest (American Heart Association)
- ACLS Secondary Survey for a Patient in Respiratory Arrest (American Heart Association)
- ACLS Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm (American Heart Association)
- ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm (American Heart Association)
- ACLS Tachycardia Algorithm for Managing Unstable Tachycardia (American Heart Association)
- ACLS Tachycardia Algorithm for Managing Stable Tachycardia (American Heart Association)
- Full text article: Neumar RW, Otto CW, Link MS, Kronick SL, Shuster M, Callaway CW, Kudenchuk PJ, Ornato JP, McNally B, Silvers SM, Passman RS, White RD, Hess EP, Tang W, Davis D, Sinz E, Morrison LJ. Part 8: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2010 Nov 2;122(18 Suppl 3):S729-67.
- Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm (American Heart Association)
- Prehospital Fibrinolytic Checklist (American Heart Association, 2010)
- Full text article: O'Connor RE, Brady W, Brooks SC, Diercks D, Egan J, Ghaemmaghami C, Menon V, O'Neil BJ, Travers AH, Yannopoulos D. Part 10: acute coronary syndromes: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2010 Nov 2;122(18 Suppl 3):S787-817.
- ACLS Suspected Stroke Algorithm (American Heart Association)
- Full text article: Jauch EC, Cucchiara B, Adeoye O, Meurer W, Brice J, Chan YY, Gentile N, Hazinski MF. Part 11: adult stroke: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2010 Nov 2;122(18 Suppl 3):S818-28.
